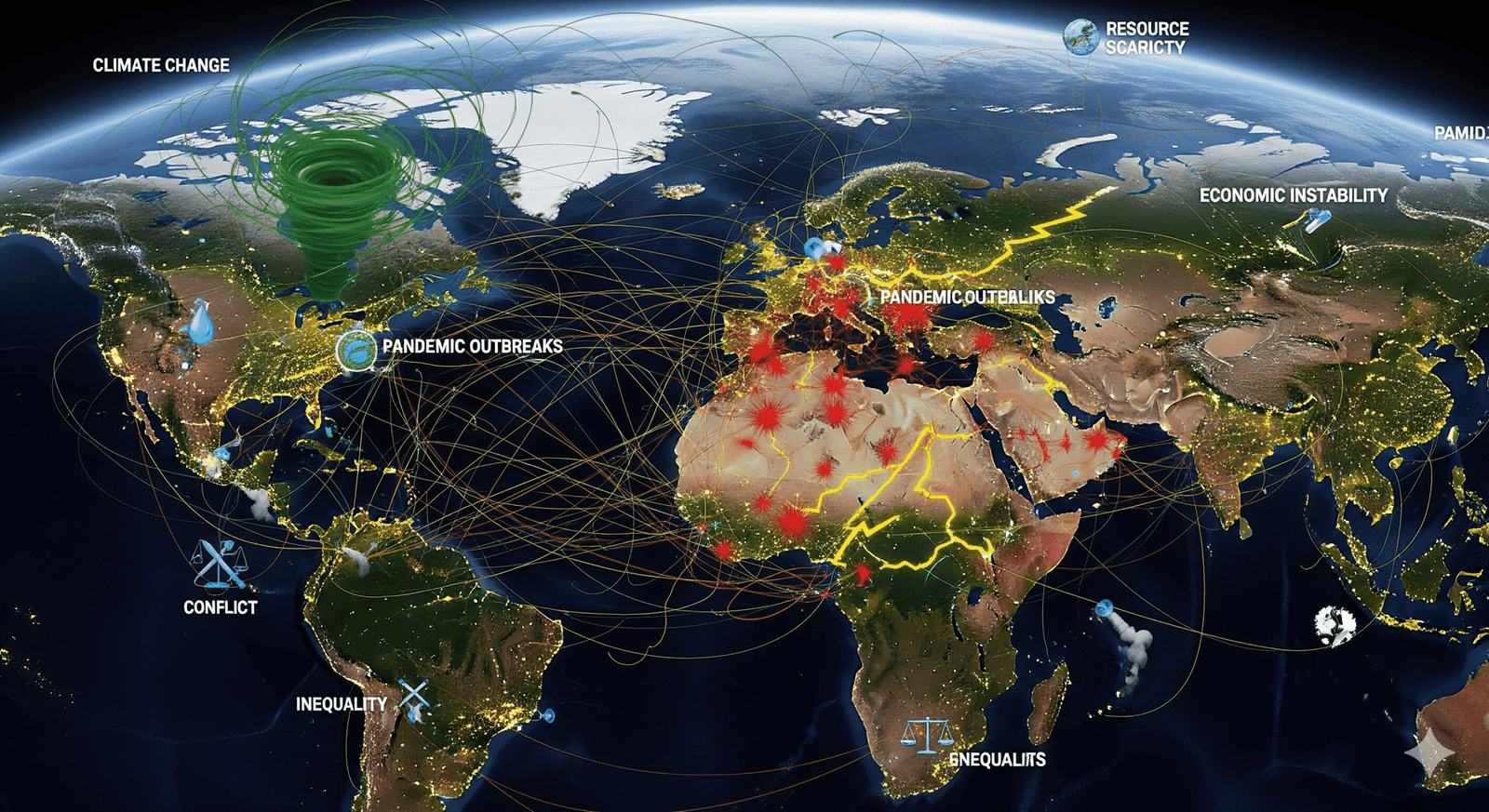
Introduction
The 21st century has reshaped the way nations interact with one another. International relations are no longer limited to traditional diplomacy between states. Today, the world faces interconnected challenges such as climate change, global health crises, migration, peace & security, sustainable development, and global trade. These issues transcend borders, forcing countries to collaborate, compete, and sometimes clash.
At the heart of these dynamics lies diplomatic relations—the art of negotiation, compromise, and representation. Whether through summits, trade agreements, or conflict resolutions, diplomacy continues to define how nations position themselves in an increasingly multipolar world.
The Evolution of International Relations
- From Cold War to Multipolarity
- The Cold War (1947–1991) defined the 20th century as a bipolar order dominated by the US and the Soviet Union.
- Post-Cold War optimism gave rise to the idea of a US-led global order.
- Today, power is dispersed—China, India, the EU, and regional blocs now influence decision-making.
- Globalization’s Role
- Global trade and technological interconnectivity accelerated interdependence.
- Example: A supply chain disruption in Asia can impact industries in Europe and North America.
- Emergence of Non-State Actors
- International organizations (UN, WHO, WTO), multinational corporations, NGOs, and even social movements now play crucial roles.
- Cultural exchange through media and digital platforms influences global perceptions.
Why Diplomatic Relations Are More Critical Than Ever
- Conflict Prevention & Peace-Building
- Diplomacy helps de-escalate tensions before they evolve into wars.
- Example: The Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA), though contested, was a landmark in using negotiations to prevent conflict.
- Global Health Diplomacy
- The COVID-19 pandemic showcased the need for cooperation in vaccine sharing and health systems support.
- “Vaccine diplomacy” became a tool of influence, with countries like China and Russia leveraging supplies for geopolitical gains.
- Climate Change and Environmental Diplomacy
- Agreements like the Paris Climate Accord highlight diplomacy’s role in addressing global crises.
- Without coordinated efforts, climate change will worsen migration, food insecurity, and conflict.
- Trade and Economic Relations
- International relations increasingly revolve around trade negotiations, tariffs, and investment treaties.
- Example: US–China trade disputes highlight the balance between cooperation and competition.
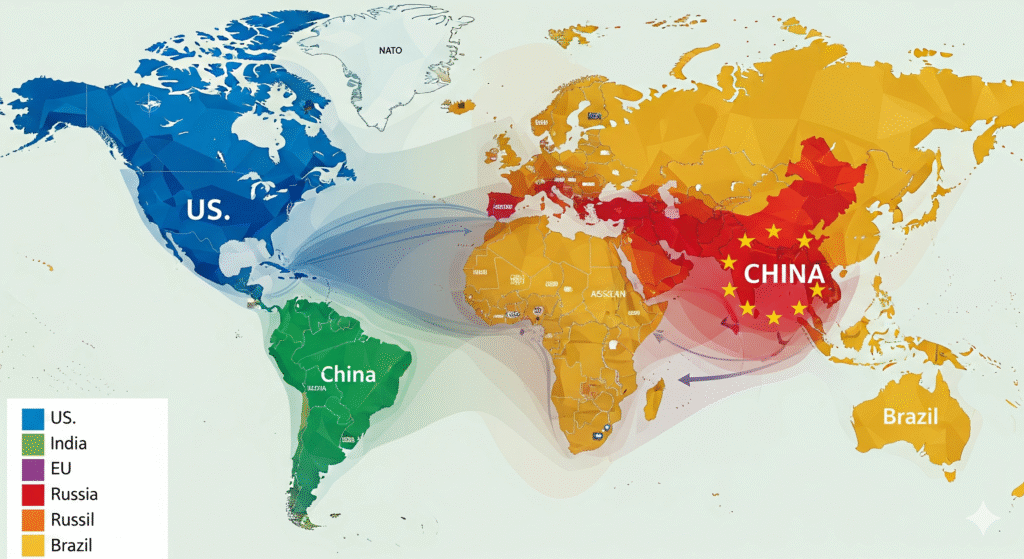
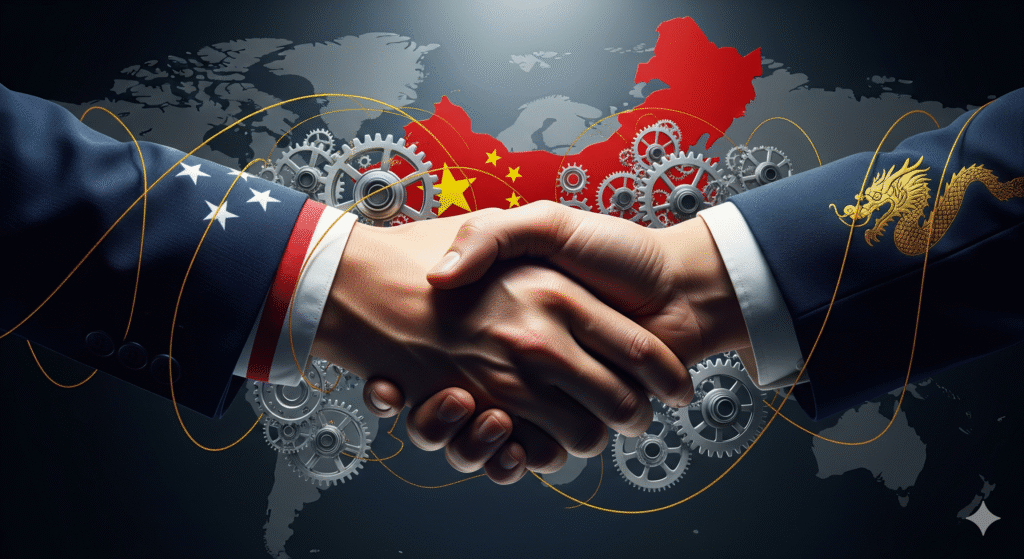
Case Study: U.S.–China Relations
- Perhaps the most defining diplomatic relationship of the 21st century.
- Cooperation: Trade, climate change agreements, global health collaboration.
- Competition: Technological supremacy, South China Sea disputes, human rights issues.
- Impact: This relationship shapes global governance, supply chains, and international security frameworks.
The Role of International Law in Diplomacy
- Framework for Peace & Security
- Treaties, conventions, and international law guide how states behave.
- Example: The Geneva Conventions protect civilians during war.
- Challenges in Enforcement
- Powerful nations often bypass or reinterpret laws for strategic interests.
- Example: Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 tested the credibility of international law and UN frameworks.
- Future of Global Governance
- Reforming institutions like the UN Security Council is crucial to ensure fair representation and legitimacy.
How Cultural Exchange Strengthens Relations
- Soft Power Diplomacy
- Beyond military or economic might, cultural diplomacy enhances influence.
- Example: South Korea’s rise in global influence through K-pop, cinema, and cultural exchange programs.
- Educational and Research Cooperation
- Student exchange programs, collaborative research, and international conferences strengthen ties beyond governments.
- Sports Diplomacy
- Events like the Olympic Games and World Cup serve as platforms for diplomacy and diversity in sports, promoting unity amid competition.

Modern Challenges in International Relations
- Rise of Nationalism and Populism
- “America First,” Brexit, and similar movements emphasize sovereignty over global cooperation.
- This threatens progress in areas like migration and humanitarian aid.
- Technology and Cybersecurity
- Cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and sports-like performance analytics applied to state surveillance alter power dynamics.
- Nations now battle in digital arenas as much as physical ones.
- Migration and Refugee Crises
- Conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and climate-driven displacement test international solidarity.
- Diplomacy must balance humanitarian needs with domestic politics.
- Inequalities in Global Governance
- Developing nations often feel sidelined in decision-making.
- Calls for more equitable sustainable development and representation in global institutions are growing louder.
Future Outlook: Diplomacy in the Next Decade
- Digital Diplomacy
- Social media and virtual platforms are reshaping how diplomats communicate.
- Example: Twitter diplomacy (“Twiplomacy”) allows leaders to directly address global audiences.
- Focus on Global Commons
- Issues like climate change, outer space, and cyber governance require collaborative frameworks.
- Shared challenges demand shared solutions.
- Multipolar Balance of Power
- Instead of one or two dominant powers, expect more regional alliances (e.g., BRICS, ASEAN, African Union).
- Integration of Humanitarian and Development Diplomacy
- Linking humanitarian aid, sustainable development, and peace & security will create more comprehensive diplomatic strategies.
Conclusion
The world is in the midst of a profound transformation. International relations and diplomatic relations are adapting to new realities shaped by multipolarity, technological disruption, climate change, and global health challenges. While conflicts, nationalism, and inequality remain barriers, diplomacy continues to be the most powerful tool for cooperation and problem-solving.
The future of global stability lies in reimagining diplomacy—not just as government-to-government negotiations but as a multidimensional effort that includes international law, cultural exchange, humanitarian aid, and global governance.
In an uncertain world, one truth stands firm: the strength of our diplomatic relations will determine whether we face global challenges divided or united.